Risks of IPv6 for Business: What They Are and How to Avoid Them

Table of contents
- Why IPv6 Matters for Business Right Now
- Top 4 Risks for Businesses
- Real-World Case: CVE-2024-38063 Vulnerability and the Cost of Unpreparedness
- How These Risks Impact Business
- Downtime and Process Interruptions
- Data Breaches
- Reputational Damage
- Rising IT Costs
- 1. Audit and Infrastructure Readiness Assessment
- 2. Setting the Right IPv6 Security Policy
- 3. Address Management and Autoconfiguration
- 4. Updating and Managing IoT Devices
- 5. Continuous IPv6 Traffic Monitoring
- 6. Training and Developing IT Staff Competencies
- 7. Business Continuity Planning and Control
- Conclusion
Internet addresses in the old IPv4 format are almost fully exhausted, and the world is gradually moving to IPv6. Your provider, partners, and customers may already be using this protocol. IPv6 brings new opportunities for businesses: it offers higher network performance, easier scaling, and a secure way to connect thousands or even millions of devices across the Internet of Things (IoT).
But rapid adoption also brings new risks. Configuration mistakes, security gaps, and network-management issues can lead to outages and data loss. This is especially relevant for companies in China, where IPv6 is implemented across the entire national infrastructure, and in fast-growing Vietnam, where digital transformation is accelerating.
This article is not a technical deep dive into protocols or standards. It is a practical guide that explains the real IPv6 risks your business may face and gives you a step-by-step plan to reduce these risks and keep your company’s operations stable right now.
Why IPv6 Matters for Business Right Now
IPv4 addresses are nearly exhausted, while the number of devices and connections is growing rapidly. If you plan to expand your business, use smart devices, or maintain a stable network, ignoring IPv6 creates real limitations.
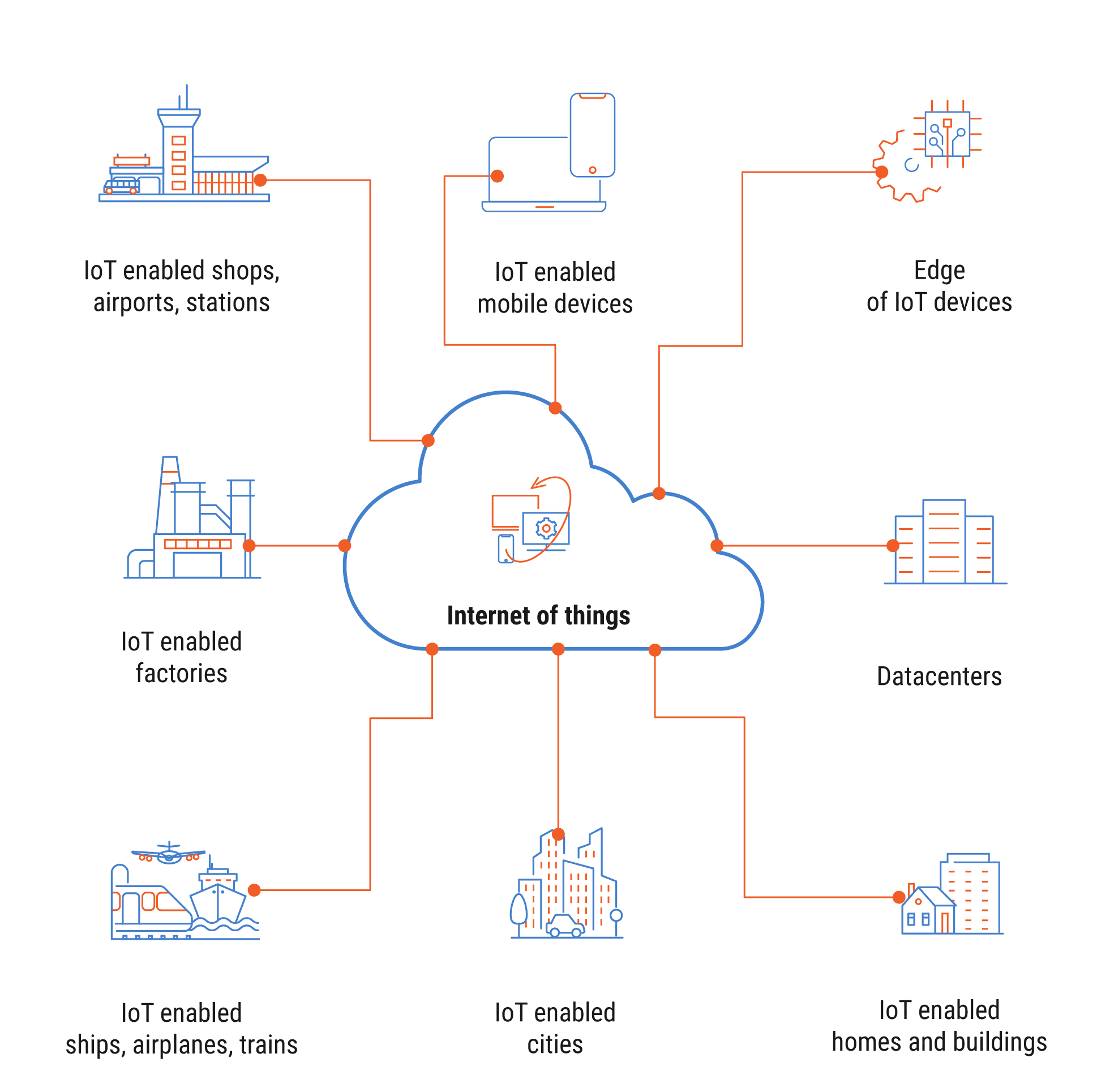
IoT Growth in Manufacturing and Logistics
The number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is growing rapidly. By the end of 2025, there are expected to be over 19 billion actively connected devices, and by 2030, up to 50 billion. Smart manufacturing systems, medical devices, logistics, energy, and consumer electronics all require unique IP addresses.
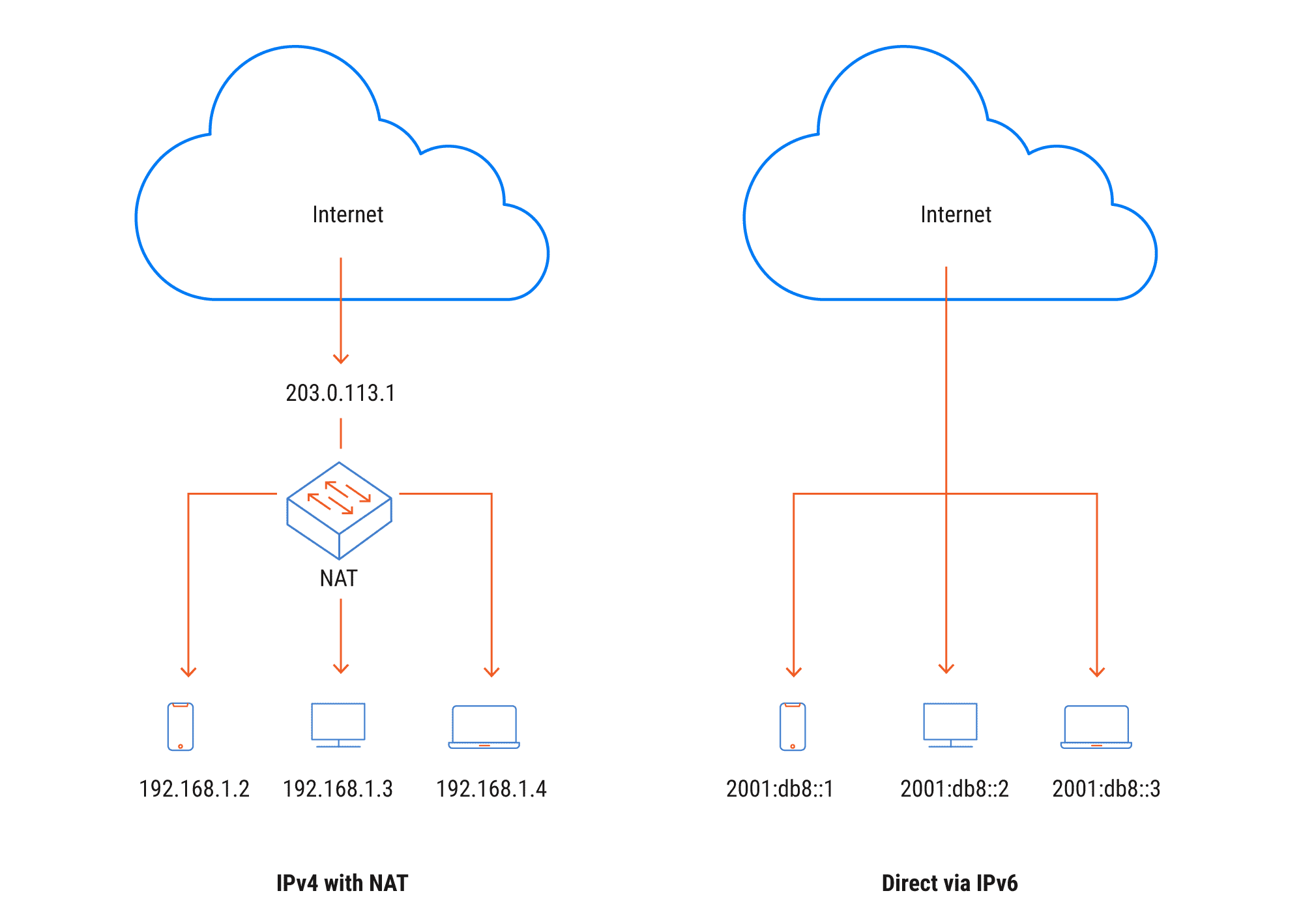
IPv4 can no longer keep up: every sensor, control system, or connected vehicle adds more demand to the already limited address space. Workarounds like NAT provide temporary relief, but a stable IoT ecosystem requires a transition to IPv6.
Strong Government Support for IPv6
Governments and regulatory bodies have started requiring IPv6 adoption. For example, the U.S. federal government mandates 80% IPv6 deployment across all devices and networks by the end of 2025. The U.S. Department of Defense issues directives requiring new network systems to support IPv6.
These requirements also apply to contractors—companies working on government contracts must support IPv6, or they risk disqualification. What began as a government initiative is quickly becoming a commercial necessity.
E-commerce and Fintech Require IP Address Scaling
Digital commerce and fintech are expanding rapidly and require a large number of IP addresses. The growing number of connections and services cannot be supported with the exhausted IPv4 space. To scale infrastructure and ensure stable business operations, IPv6 has become essential.
Ignoring IPv6 can limit network expansion, create issues when connecting new IoT devices, and complicate the operation of digital services.
Top 4 Risks for Businesses
We’ve looked at why IPv6 is becoming critical for business stability and growth. Now it’s time to examine the specific risks that arise from ignoring it. Each of these risks can impact network performance, data security, and the efficiency of business processes.
Risk #1: Lack of Skills and Expertise for Working with IPv6 from Deployment to Troubleshooting
Deploying and managing IPv6 requires new skills and knowledge. Most engineers and administrators are accustomed to IPv4 and lack practical experience with IPv6 configuration, dual-stack networks, transition mechanisms, and new security features. Configuration mistakes can lead to network outages or security gaps.
Factors Increasing the Risk: the IT market is growing rapidly, but there is a shortage of qualified professionals with hands-on IPv6 experience. Small and medium-sized businesses are particularly vulnerable: they often lack internal teams to prepare and maintain IPv6 networks and must rely on costly consultants or a limited pool of certified engineers.
Business Consequences:
- IPv6 misconfigurations create security vulnerabilities and can trigger network incidents.
- Service downtime and network failures result in productivity losses and reduced customer service quality.
- Additional costs for urgent training, certification, or hiring specialists raise operational and financial expenses.
- Lack of skilled staff slows down the deployment of new digital services and infrastructure scaling.
Business Takeaway: Without investment in IPv6 training and expertise development, organizations remain vulnerable, face higher risks of outages and security issues, and lose flexibility in expanding their digital infrastructure.
Risk #2: Compatibility of Hardware and Applications
Many existing routers, switches, firewalls, security devices, and enterprise applications were designed for IPv4 and either do not support IPv6 or support it only partially. Some devices may not function with IPv6 even after firmware updates, and older applications or embedded systems may operate incorrectly in a dual-stack environment.
Factors Increasing the Risk: long equipment lifecycles in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and finance increase the likelihood that infrastructure is outdated and needs upgrades to support IPv6.
Business Consequences:
- Significant capital expenditures for hardware replacement and software upgrades.
- Delays in IPv6 deployment due to testing and adapting infrastructure.
- Risk of failures in critical applications and embedded systems, potentially impacting production, logistics, and service quality.
- Additional operational challenges when integrating new systems with existing infrastructure.
Business Takeaway: Without assessing hardware and application compatibility, IPv6 deployment can become expensive, complex, and risky, potentially disrupting business services.
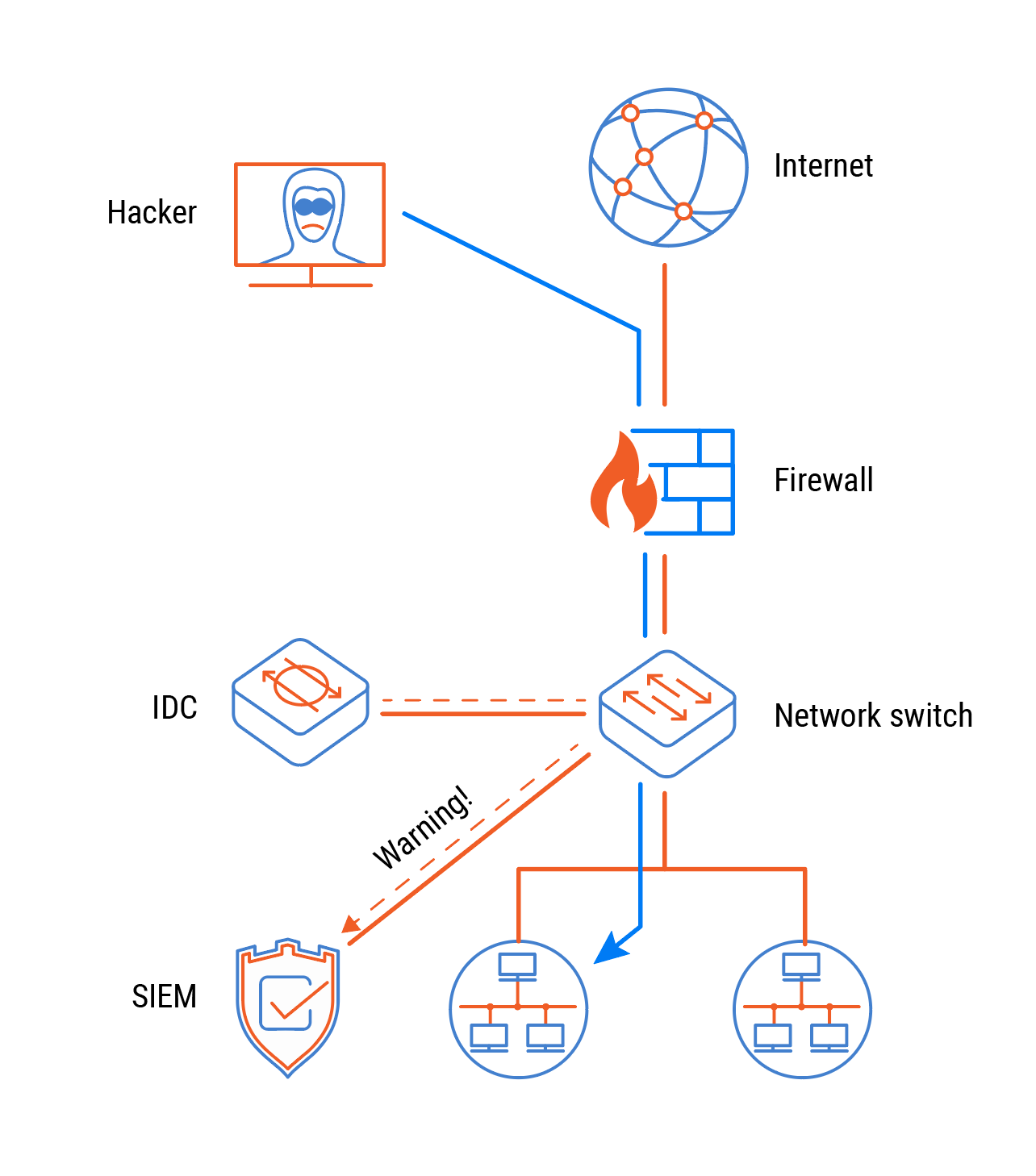
Risk #3: Challenges in Monitoring and Security
Network monitoring, intrusion detection, and prevention systems designed for IPv4 often do not provide full visibility into IPv6 traffic. Many IDS, IPS, and SIEM tools have limited IPv6 support and fail to detect attacks specific to IPv6.
Factors Increasing the Risk: lack of IPv6 knowledge and experience among security specialists, absence of processes and tools for comprehensive IPv6 monitoring, and reliance on outdated solutions without full support for the new protocol.
Business Consequences:
- Attacks and incidents may go unnoticed, increasing the risk of data and system compromise.
- Delays in identifying vulnerabilities and responding to incidents can lead to financial and reputational losses.
- Lack of IPv6 traffic control raises the likelihood of exploitation through new attack vectors not covered by existing security measures.
Business Takeaway: Without adapting monitoring tools and security processes for IPv6, an organization remains “blind” to new threats, directly impacting business stability and protection.
Risk #4: Hidden Vulnerabilities and Failures in Dual-Stack Networks
The most dangerous period is not before or after switching to IPv6, but during the transition, when networks operate in a hybrid (Dual-Stack) mode, supporting both protocols simultaneously. In this environment, IPv4 and IPv6 run in parallel, creating unpredictable failure points, security blind spots, and making troubleshooting extremely complex. Misconfigurations between the two protocols, application malfunctions, or incomplete monitoring coverage in a Dual-Stack network can halt critical business processes.
Factors Increasing the Risk: most IT teams lack hands-on experience with operating and securing Dual-Stack networks. Legacy applications and hardware not tested for hybrid environments behave unpredictably. Additionally, security policies and monitoring systems configured for IPv4 often ignore IPv6 traffic, creating ideal conditions for cyberattacks. This turns the planned transition into a period of maximum vulnerability.
Business Consequences:
- Unexpected downtime of critical systems: Production lines, accounting systems, or online platforms may stop due to protocol conflicts or errors in the hybrid configuration that cannot be quickly diagnosed.
- Data leaks through “blind spots”: Attackers exploit unprotected IPv6 channels while defenses focus on IPv4. Sensitive data can be exposed without detection.
- High costs for urgent troubleshooting and fixes: Diagnosing and resolving issues in a Dual-Stack environment requires specialized expertise. A shortage of such specialists leads to prolonged downtime and expensive external consulting.
- Reputational damage from instability: Clients and partners lose trust in a company whose services falter during the “technical transition” period.
Business Takeaway: A Dual-Stack hybrid environment is not just “turning on a new technology” — it is a zone of heightened operational and financial risk. Without a dedicated plan for management, security, and testing during this phase, a company deliberately exposes itself to large-scale failures, data leaks, and reputational loss. Dual-Stack risk management must be a core part of any IPv6 transition strategy.
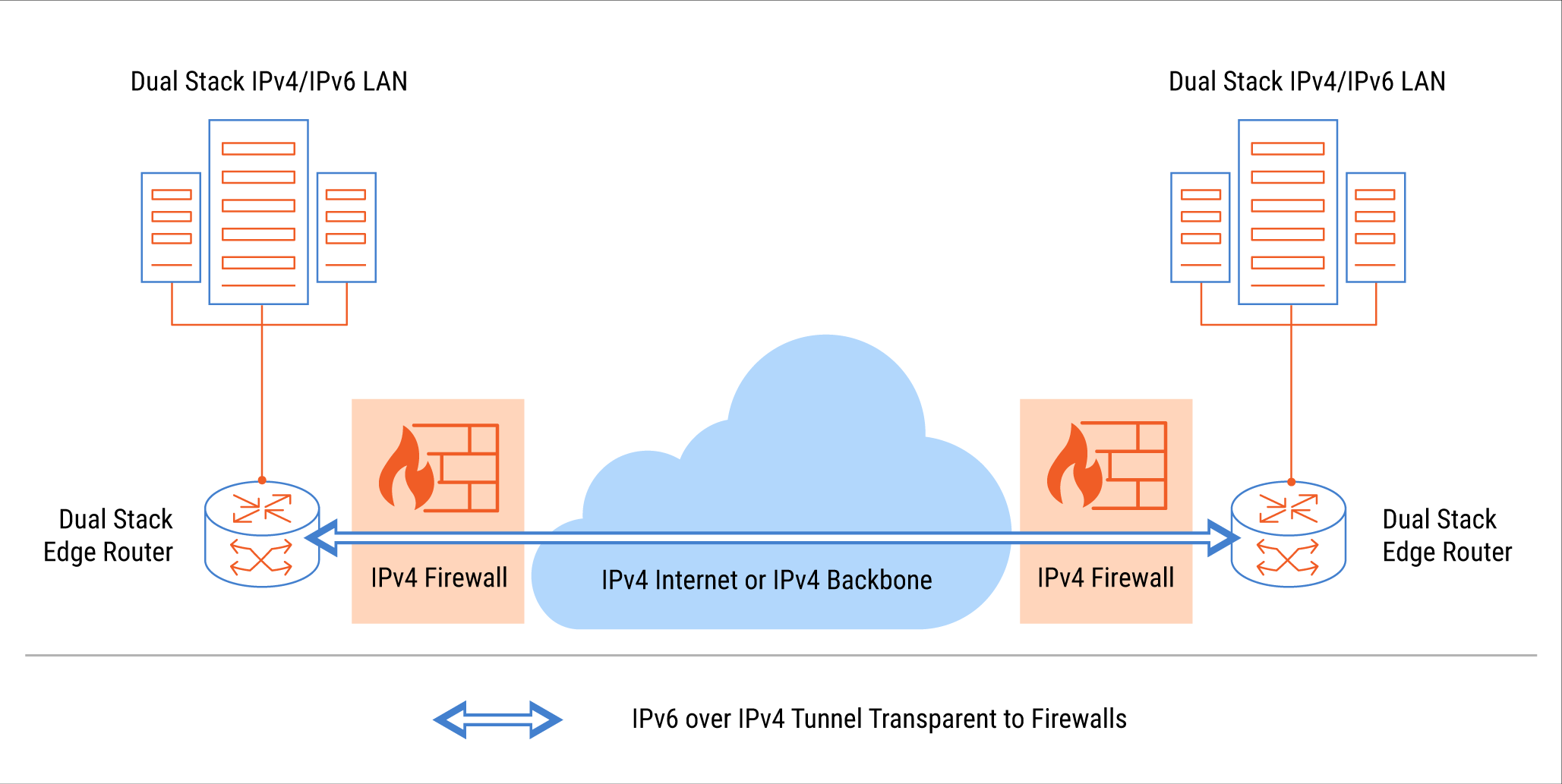
Real-World Case: CVE-2024-38063 Vulnerability and the Cost of Unpreparedness
In August 2024, an incident was revealed that clearly demonstrated all the risks described above. It involved a critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-38063) in the Windows kernel affecting IPv6 traffic processing. This situation was not just a technical note—it became a full-fledged business case illustrating the consequences of failing in strategic preparation.
What Happened
A serious security flaw related to IPv6 was discovered in the most widely used operating systems—from Windows 10 to server editions. The vulnerability allowed an attacker to remotely compromise a system simply by sending a specially crafted network packet, without any action required from the user.
Market Reaction: Both Indicative and Mistaken
Microsoft, the developer, recommended as an emergency measure to completely disable IPv6 to reduce risk. Many companies, viewing IPv6 as a “secondary option” or “future technology”, followed this advice.
Why this decision became a strategic mistake and increased risks:
- Admission of unpreparedness: Disabling IPv6 does not fix the security issue; it signals that infrastructure and teams are not ready to manage it. Companies voluntarily forfeit a protocol critical for future growth.
- Creation of a “blind spot”: With IPv6 disabled at the settings level, organizations lose visibility and control. Attackers can use tunneling (hidden IPv6 traffic inside IPv4) to bypass defenses and target systems that administrators believe are protected.
- Direct operational losses: For companies already deploying IoT or relying on modern network services, this action could halt new business processes.
- Deferred but increased costs: Once the vulnerability is patched, IPv6 must be re-enabled. Doing so under pressure, without full understanding of the network, leads to unplanned expenses and new risks of failures.
What This Means for Your Business
The CVE-2024-38063 incident is not an anomaly but a predictable outcome of treating IPv6 as an “optional feature.” It clearly demonstrated:
- Lack of expertise leads to panic-driven, harmful decisions: Well-prepared teams could have applied targeted security rules instead of completely rolling back the technology.
- Blind spots often exist where you think the system is “off”: Without full IPv6 traffic monitoring, threats go unnoticed.
- Reactive rather than proactive IPv6 management harms operational resilience: Companies with a clear IPv6 development and monitoring plan weathered the incident with minimal impact, simply updating systems. Others were forced into strategically disadvantageous decisions.
Business Takeaway: Incidents like this will recur. The question is whether your company will face them as a controlled event within a well-thought-out strategy or as an emergency requiring tactical retreat, causing real financial and reputational damage. IPv6 readiness is not just ticking a box in settings—it requires a comprehensive system: trained teams, adapted security tools, and a phased implementation plan.
How These Risks Impact Business
Transitioning to IPv6 is no longer just a network modernization issue—it is a strategic decision that directly impacts a company’s financial stability, operational efficiency, and reputation. The technical risks discussed earlier — IPv4 limitations, configuration errors, lack of expertise, dual-stack vulnerabilities, and compatibility problems—do not remain “inside IT.” They immediately affect business operations, turning into real threats to processes, revenue, data, and customer trust.
In today’s digital world, networks are the heart of business. Any disruption, even local and short-term, can trigger cascading consequences: production stops, e-commerce downtime, data leaks, lost customers, and increased remediation costs. In this section, we translate technical risks into business terms, showing the tangible consequences they create here and now.
Each business risk is linked to a specific technical problem, but the focus here is on what that problem means for the company: lost revenue, decreased productivity, regulatory fines, loss of customer trust, and higher expenses. Understanding this connection helps executives view IPv6 not as an abstract IT task but as a real threat to operational continuity and strategic growth.
Below are the key business risks arising from ignoring IPv6 adoption, with explanations of how they manifest in practice and recommendations for mitigating their impact on the company.
Downtime and Process Interruptions
This risk is directly linked to insufficient staff preparation for working with IPv6, configuration errors in network devices, and challenges in managing dual-stack networks. Technical issues that may seem minor to the IT team can quickly escalate into major business disruptions if critical processes depend on continuous network operation.
Business Impact: Modern companies rely heavily on stable network infrastructure. Production lines, warehouse logistics systems, automated sales systems (POS), and e-commerce platforms operate only when the network runs continuously. Any conflict between IPv4 and IPv6, incorrect device configuration, or an exploited IPv6 vulnerability can halt key business processes.
For business, this means that even a short-term outage can translate into real financial losses. For example, downtime on a production line can lead to missed deliveries, breach of contractual obligations, and potential fines from partners. In retail or e-commerce, a few hours of POS system or online platform downtime reduces revenue, triggers returns, and generates negative customer feedback.
A line or order-receiving system being down for just a few hours is not merely an IT technical issue. It results in lost products, revenue, breached contracts, and reduced customer trust. If such an incident repeats, the reputational damage can far exceed the financial loss from a single outage.
Why This Matters: In today’s business environment, time is money. Companies delaying IPv6 adoption effectively put the stability of critical processes at risk. Technical mistakes or lack of expertise—problems that could have been prevented—become direct threats to operational continuity.
Recommendations:
- Conduct an audit of current network infrastructure to assess IPv6 readiness.
- Verify that critical systems function correctly in a dual-stack environment.
- Develop and implement disaster recovery and downtime-minimization plans.
- Provide staff training and prepare IT teams to manage IPv6 and dual-stack networks.
Business Takeaway: IPv6-related downtime translates directly into business losses. Timely preparation, audits, and team training reduce operational risks and ensure continuity of business processes — especially critical for manufacturing, logistics, and retail companies.
Data Breaches
Data breaches are directly linked to weaknesses in IPv6 monitoring and security, misconfigured address management, and the exploitation of vulnerabilities in dual-stack networks. Technical “gaps” that go unnoticed by IT teams can give attackers access to sensitive information, turning into real and significant business risks.
Business Impact: Confidential company data—financial information, personal data of customers and employees, and trade secrets—depends directly on the correct operation of the network infrastructure. IPv6 configuration errors, insufficient use of monitoring tools, or improper operation of dual-stack networks can allow attackers to intercept traffic, bypass security controls, or deploy malware.
For business, this means that any unsecured point in the network becomes a potential threat. A data breach can lead to regulatory fines, loss of customers and partner trust, and additional costs for investigation and recovery. In sectors such as finance, e-commerce, and healthcare, the consequences can be especially severe due to strict requirements for protecting personal data.
Every data breach is not just a technical incident. It is a direct hit to the budget, reputation, and customer trust. Unauthorized access to financial or personal data can result in fines, lawsuits, and serious reputational damage that is difficult to recover from.
Why This Matters: In modern business, data security is a strategic asset. Ignoring IPv6-related threats leaves a company vulnerable to attacks that are invisible to standard IPv4-focused monitoring tools. Early identification of weak points and proper security processes not only help prevent data breaches but also reduce potential financial and reputational losses.
Recommendations:
- Implement full IPv6 traffic monitoring and integrate it into the overall security system.
- Review and update address management processes, including IPv6 autoconfiguration and dual-stack networks.
- Regularly train staff on IPv6 operations and modern security tools.
- Plan and test attack scenarios and incident response procedures to minimize damage in case of unexpected events.
Business Takeaway: Underestimating IPv6 security risks has a direct impact on a company’s financial performance and reputation. A comprehensive approach to monitoring, protection, and staff training reduces the likelihood of data breaches and provides confidence in the security of critical business processes.
Reputational Damage
Reputational damage is directly linked to service downtime, application failures, and security incidents caused by misconfigured IPv6, dual-stack networks, or lack of monitoring. Technical issues that go unnoticed or are poorly managed quickly turn into real threats to a company’s public image.
Business Impact: In today’s digital environment, a company’s reputation is shaped online. Web application outages, IoT device failures, unstable service performance, and data breaches immediately affect the trust of customers and partners. Even short-term issues can lead to negative reviews, customer churn, and strained partner relationships. In sectors such as e-commerce, fintech, and healthcare, such incidents can cause long-term brand damage and loss of competitive advantage.
Every unavailable service or system failure is not just a technical issue. It results in lost customer loyalty, negative reviews, reduced partner trust, and a potential decline in market position. A reputation built over years can be damaged in a matter of hours.
Why This Matters: Reputation has a direct impact on financial performance and a company’s strategic opportunities. Customers and partners expect reliable services and strong data protection. Ignoring IPv6-related issues creates an invisible but critical vulnerability that can cause serious reputational and financial damage.
Recommendations:
- Plan redundancy and high availability for critical services to minimize downtime.
- Test dual-stack networks and verify IPv6 compatibility of applications and IoT devices.
- Develop and rehearse rapid incident response scenarios, including communication with customers and partners.
- Implement continuous service availability monitoring and tools to detect network anomalies.
Business Takeaway: Reputational damage is a direct result of technical gaps and insufficient IPv6 readiness. Timely testing, redundancy, and the ability to respond quickly help companies maintain the trust of customers, partners, and investors, ensuring long-term business resilience.
Rising IT Costs
Rising IT costs are a direct result of technical challenges: the need to upgrade legacy hardware, hire specialists with IPv6 experience, implement monitoring and security processes, and adapt applications and IoT devices to the new protocol.
Business Impact: Transitioning to IPv6 without a well-thought-out plan often becomes a source of unexpected expenses. Emergency hardware purchases, unplanned consultant fees, staff training, software updates, and IoT device integration create financial burdens that can exceed the planned budget. This is especially critical for companies with a large number of network devices and complex infrastructure, where delays and planning errors are costly.
Ignoring IPv6 today leads to high costs tomorrow. Emergency upgrades, hiring specialists, and fixing errors can consume budget allocated for strategic business growth and slow down the execution of key projects.
Why This Matters: Unpredictable IT expenses reduce a company’s financial flexibility, limit resources for innovation and growth, and increase the risk of operational disruptions due to inadequately prepared infrastructure.
Recommendations:
- Plan the budget in advance for network equipment upgrades, including routers, switches, and security devices.
- Prepare the team through IPv6 training and certification.
- Implement processes to ensure application and device compatibility with IPv6 to avoid sudden costs for emergency adjustments.
- Assess long-term expenses and potential risks so that the IPv6 transition is a manageable and predictable process.
Business Takeaway: Rising IT costs are not an abstract threat—they are a real financial risk. Timely planning and preparation for IPv6 adoption help optimize expenses, reduce the likelihood of unexpected costs, and ensure sustainable business growth.
Protecting Your Business: Practical Solutions
Ignoring IPv6 is not just an IT technical issue—it is a strategic vulnerability that affects operational stability, financial performance, and company reputation. However, these risks can be managed and minimized through systematic, proactive action. IPv6 security is an ongoing process that includes auditing, planning, training, and continuous monitoring.
Below is a step-by-step set of actions to help your organization turn potential threats into manageable business processes.
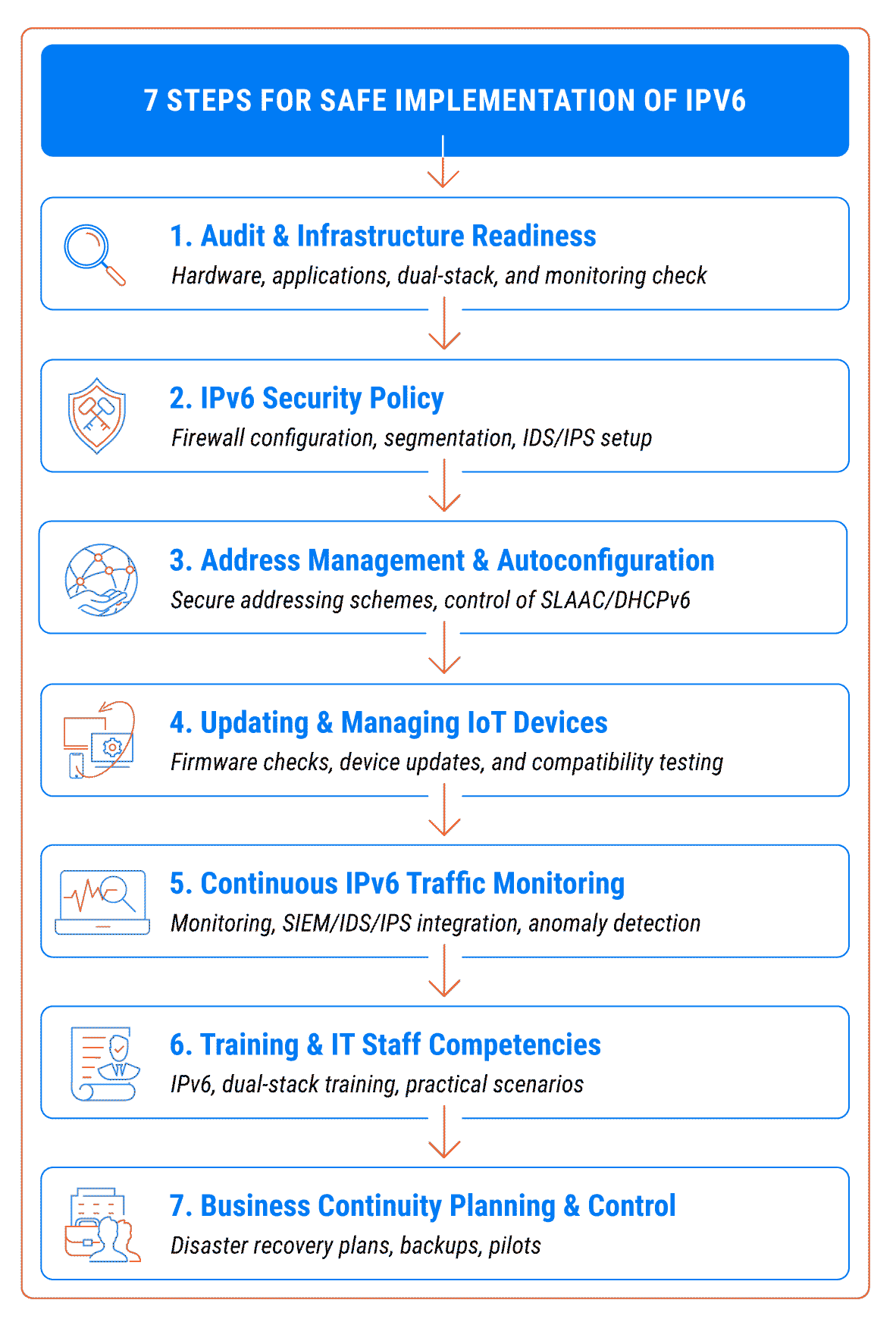
1. Audit and Infrastructure Readiness Assessment
Before deploying IPv6, it’s essential to understand the current state of your network infrastructure. This includes:
- Analyzing hardware and application compatibility with IPv6.
- Checking dual-stack network configurations and identifying bottlenecks.
- Evaluating the capabilities of existing monitoring and security systems for IPv6 support.
Why This Matters: Auditing helps identify weak points that could lead to downtime, data leaks, or service disruptions, allowing you to plan remediation before active deployment.
2. Setting the Right IPv6 Security Policy
Devices and networks must be protected as rigorously as they are for IPv4:
- Configure IPv6 firewalls and network segmentation.
- Develop security policies for dual-stack environments.
- Verify proper operation of monitoring tools and IDS/IPS with IPv6 traffic.
Why This Matters: Protecting IPv6 traffic prevents hidden threats and reduces the risk of incidents that could impact business processes and company reputation.
3. Address Management and Autoconfiguration
Proper IPv6 address management minimizes risks:
- Use secure addressing schemes and privacy extensions.
- Control autoconfiguration (SLAAC, DHCPv6) to prevent predictable patterns.
- Integrate address management processes into overall monitoring and security systems.
Why This Matters: Mistakes at this stage create potential attack vectors and increase the risk of data leaks.
4. Updating and Managing IoT Devices
- Check firmware and capabilities of devices for IPv6 support.
- Schedule updates for outdated devices.
- Test IoT devices and critical applications for compatibility in a dual-stack environment.
Why This Matters: IoT and embedded systems rely heavily on unique addresses and proper network interaction. Non-compliance with IPv6 standards can lead to process interruptions and reputational damage.
5. Continuous IPv6 Traffic Monitoring
- Implement monitoring and analytics systems for IPv6 traffic.
- Integrate with existing security tools (SIEM, IDS/IPS).
- Track anomalies and prepare incident response scenarios.
Why This Matters: Early detection of threats and failures helps minimize financial and reputational losses.
6. Training and Developing IT Staff Competencies
- Provide targeted training on IPv6, dual-stack networks, and secure configuration.
- Develop internal competence centers.
- Conduct regular practical exercises and pilot deployment scenarios.
Why This Matters: A skilled team minimizes configuration and operational errors, reducing the risk of downtime and data leaks.
7. Business Continuity Planning and Control
- Develop disaster recovery plans and redundancy for critical services.
- Integrate IPv6 into strategic planning for procurement, training, and security processes.
- Conduct pilot deployments to identify issues and train staff.
Why This Matters: A systematic approach transforms IPv6 adoption from a reactive project into a managed strategic initiative, reducing unexpected costs and increasing the business’s readiness for scaling.
Ensuring your IPv4 and IPv6 infrastructure is correctly set up and maintained minimizes downtime and security risks. Expert support from IPTP Networks is available if required — Learn more about IPv4/IPv6 Services.
Conclusion
IPv6 is no longer a topic for the future — it is a present reality for businesses. IPv4 addresses are running out, IoT devices are multiplying, regulatory requirements are tightening, and new IPv6 vulnerabilities continue to emerge. All of this creates real risks for network operations, data security, and business processes.
Companies that prepare in advance — checking equipment compatibility, training staff, and setting up IPv6 monitoring and security — experience the transition smoothly, with controlled costs and minimal disruptions.
Those that postpone adoption face unexpected expenses, outages, and security threats. Today, the question is not whether to adopt IPv6, but how to do it: proactively and strategically, or reactively under pressure. The approach you choose determines your company’s stability, competitiveness, and financial resilience.